In today’s digital landscape, organizations must navigate complex security challenges to protect their data and systems. However, many professionals and decision-makers often confuse the terms Information Security Governance and Cybersecurity, treating them as interchangeable concepts. While both are crucial for safeguarding digital assets, they serve distinct purposes and operate at different levels within an organization.
The Relationship Between ISG and Cybersecurity
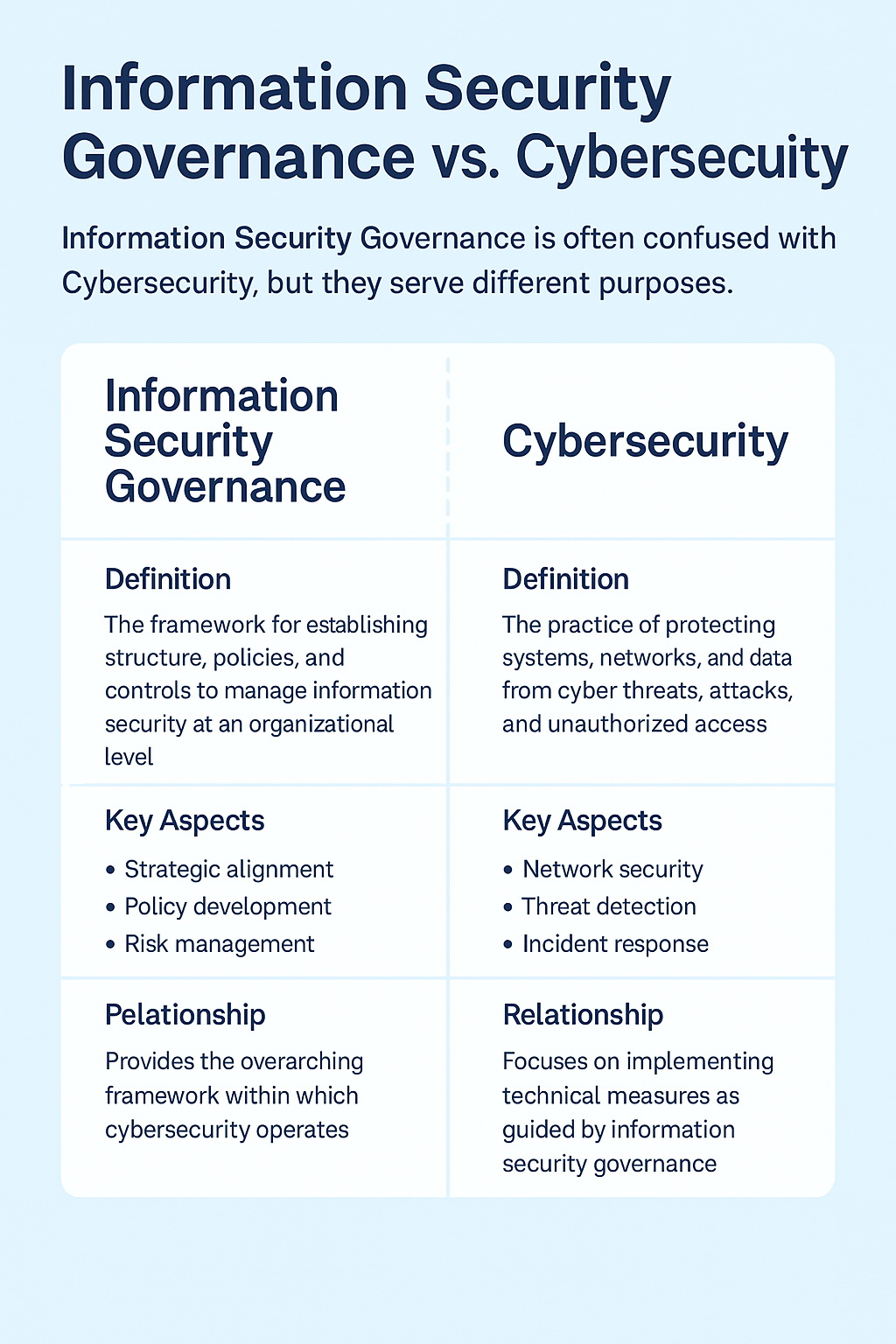
While ISG and cybersecurity have different functions, they are interdependent. Strong cybersecurity measures rely on effective governance to define policies and frameworks, while governance depends on cybersecurity to implement and enforce security strategies.
For example, an organization with well-established Information Security Governance will set security policies and define risk management strategies. These policies will then guide cybersecurity teams in deploying security controls, monitoring threats, and responding to incidents effectively.
What Is Information Security Governance?
Information Security Governance (ISG) refers to the strategic framework that ensures an organization’s security objectives align with its business goals. It encompasses policies, risk management, compliance, and oversight mechanisms that guide how information security is managed within an organization.
Key Aspects of ISG:
- Strategic Planning – Establishes security policies, goals, and objectives aligned with business needs.
- Risk Management & Compliance – Identifies, assesses, and mitigates security risks while ensuring adherence to regulations (e.g., GDPR, ISO 27001, NIST).
- Roles & Responsibilities – Defines leadership roles, accountability, and decision-making structures for security governance.
- Performance Monitoring – Evaluates security effectiveness through audits, metrics, and compliance assessments.
Why ISG Matters:
Effective Information Security Governance ensures that cybersecurity efforts are not reactive but proactively managed at an organizational level. Without governance, security investments may lack direction, leading to gaps in protection and inefficient resource allocation.
What Is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity focuses on the technical measures and processes used to protect digital assets from cyber threats, attacks, and unauthorized access. It involves implementing security controls, monitoring threats, and responding to incidents.
Key Aspects of Cybersecurity:
- Network Security – Protects networks from unauthorized access, malware, and data breaches.
- Endpoint & Application Security – Ensures software, systems, and devices are hardened against cyber threats.
- Threat Intelligence & Incident Response – Detects, investigates, and mitigates security incidents in real-time.
- Security Technologies – Implements tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and encryption to safeguard data.
Why Cybersecurity Matters:
Without robust cybersecurity, organizations are vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and financial losses. However, cybersecurity operates at a more tactical and operational level, focusing on technical defenses rather than overarching security governance.
Key Differences Between ISG and Cybersecurity
| Information Security Governance | Cybersecurity | |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Strategic security management, policies, and risk frameworks | Technical protection, threat mitigation, and security controls |
| Scope | Broad, organization-wide security oversight | Specific to IT infrastructure and digital assets |
| Responsibility | Senior leadership, board members, security executives | Security analysts, engineers, and IT teams |
| Compliance & Risk | Ensures regulatory compliance and risk management | Implements controls to address specific security risks |
| Decision-Making Level | High-level policy and governance framework | Operational and technical security measures |
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between Information Security Governance and Cybersecurity is essential for building a comprehensive security program. Governance provides the strategic direction, ensuring security efforts align with business objectives, while cybersecurity executes the technical defenses to protect digital assets. Organizations must integrate both elements to create a resilient and well-structured security posture.
By recognizing their unique roles and interconnections, businesses can improve their security frameworks, ensure compliance, and enhance their ability to prevent and respond to cyber threats.





Leave A Comment